Legal Literacy - This article discusses the importance of personal data protection in Indonesia and the challenges faced in implementing existing laws and regulations. Despite legislative advances, such as Law Number 27 of 2022 concerning Personal Data Protection and other regulations, there are still many shortcomings in the application of this law which lead to the risk of personal data hacking and privacy violations.
This article also explains the types of data considered sensitive, including biometric and financial data, and how this data must be protected by electronic system provider companies. Furthermore, it also describes the responsibilities of companies and the rights and obligations of consumers in the face of data breaches. Dispute resolution through litigation and non-litigation channels such as BPSK is also considered as a way to enforce consumer rights. The conclusion of the article emphasizes the importance of cooperation between sectors and increasing public awareness about the importance of data protection.
Introduction
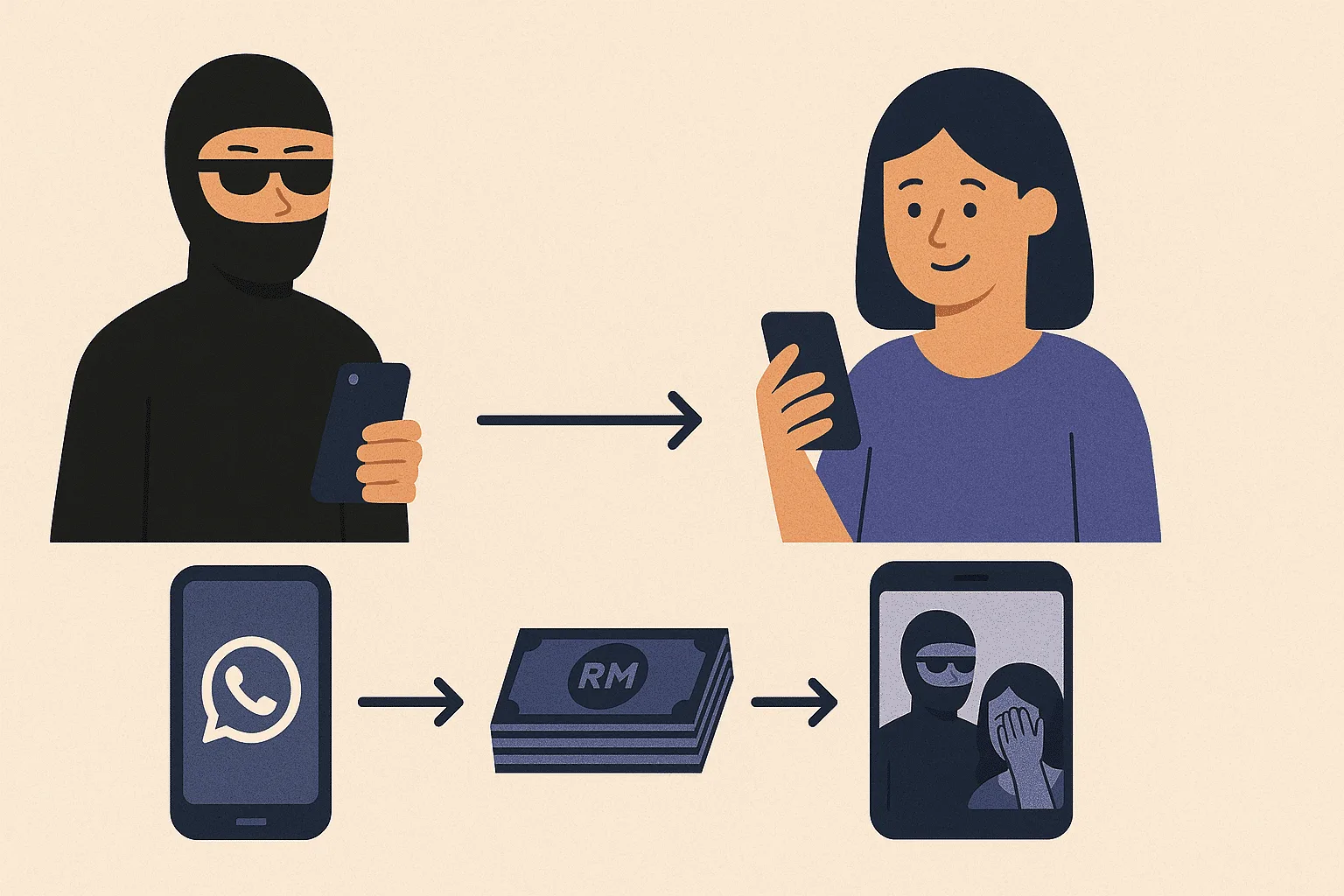
In today's digital era, technology has become an essential component of everyday life. However, this technological advancement also brings significant risks, including cybercrime that often involves the theft of personal data. In Indonesia, the existence of regulations regarding personal data protection is a frequently debated topic regarding its effectiveness in protecting individual rights.
What is Personal Data?
Personal data is information that can be used to identify individuals either directly or indirectly. This type of data includes:
- Name and address
- Identification numbers such as KTP (Resident Identity Card), passport, and telephone number
- Location data, including home address or email address
- Biometric data such as fingerprints and facial images
- Medical and financial information
- Education and employment records
- Data generated from online activities such as IP addresses and internet browsing history
Personal Data Protection Regulations
Data privacy laws in Indonesia establish a legal framework for the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data. Key regulations include Government Regulation Number 80 of 2019 concerning Trading Through Electronic Systems and Law Number 27 of 2022 concerning Personal Data Protection. Despite legislative efforts, there remain gaps in implementation and a lack of stringent legal sanctions for violations.
Responsibilities of Electronic System Providers
In the event of a data breach, companies that operate electronic systems have legal responsibilities to their consumers. Consumers who agree to the "terms of service" form a legal agreement that protects their rights in the event of a violation.
How to Resolve Disputes
Consumers who are harmed by personal data breaches have several options for dispute resolution:
- Litigation Path: Filing a civil lawsuit in court.
- Non-Litigation Path: Mediation, arbitration, or conciliation through the Consumer Dispute Resolution Agency (BPSK).
Conclusion and Call to Action
Personal data protection requires cooperation between the government, companies, and the public. The importance of revising and improving regulations is key to addressing challenges in the digital age. The public also needs to increase awareness and knowledge of their rights as consumers.



























Comments (0)
Write a comment